Transformers are essential electrical devices used in power distribution and transmission systems to step up or step down voltage levels efficiently. Transformers consist of several key components, each serving a specific function to ensure the proper operation and safety of the transformer. In this article, we will explore the various parts of a transformer and their functions in detail.
Core:
The core of the transformer is usually made of laminated sheets of high grade electrical steel. Its main function is to provide a low reluctance path for the magnetic flux generated by the primary winding. The design and material of the core helps reduce core losses due tsteresis and eddy currents, improving the overall efficiency of the transformer.
Windings:
Transformers have two types of winding: primary winding and secondary winding. The primary winding receives electrical energy from the power source, while the secondary winding delivers the converted output voltage to the load. The windings consist of insulated copper conductors wound around the core. The number of turns in each winding determines the transformer's turns ratio and voltage conversion capabilities.
Tank:
The tank is the outer wall of the transformer, usually made of steel. Its main function is to provide mechanical support and protection to the internal components of the transformer such as core and windings. This tank also acts as a barrier to prevent leakage of transformer oil.
Insulation:
Insulation is very important in transformers to prevent electrical faults and ensure electrical safety. Insulating materials, such as paper, pressboard, or synthetic materials, are used to separate the windings and provide insulation between the various components of the transformer. Insulation prevents short circuits and ensures that electricity flows through the intended paths.
Transformer Oil:
Transformer oil, also known as insulating oil, serves several functions in a transformer. It acts as both an electrical insulator and a cooling medium. Oil provides electrical insulation between the windings and the core, preventing arcing and electrical faults. Additionally, it absorbs and dissipates the heat generated during the operation of the transformer, helping to maintain the temperature of the transformer within safe limits.
Terminals and bushings:
Terminals and bushings are used to connect external electrical circuits to the windings of the transformer. The terminals are the connection points for the primary and secondary windings, while the bushings provide an insulating pass-through for the high-voltage conductors.
Breather:
A breather is a device that helps keep the internal environment of the transformer dry and moisture-free. It contains silica gel or other desiccant material that absorbs moisture from the air entering the transformer during temperature fluctuations.
Tap Changer:
Tap changers are used to adjust the turns ratio of the transformer and regulate the output voltage. They allow tapping into different points along the winding, enabling voltage adjustment to match different load conditions.
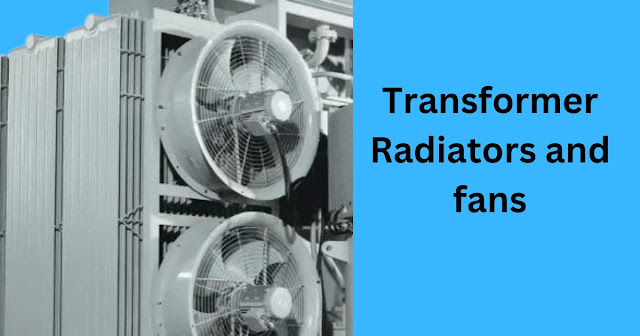
Radiators and fans:
Large transformers are fitted with radiators and fans to enhance cooling. Radiators are heat exchangers that transfer heat from the transformer oil to the surrounding air, and fans facilitate airflow over the radiators, improving cooling efficiency.
Buchholz Relay:
Buchholz relay is a protective device installed in large transformers. It detects and signals abnormal conditions, such as internal faults, oil flow problems, or gas accumulation, providing an early warning to prevent damage to the transformer.
Explosion vents and pressure relief devices(PRDs):
These protective devices are used to release excessive pressure that may build up inside the transformer during abnormal conditions, such as internal faults or overheating. By releasing pressure, they prevent catastrophic failure and ensure the safety of personnel and equipment.
Oil Conservator Tank:
The oil conservator tank is a reservoir located above the main transformer tank. This allows the transformer oil to expand and contract due to temperature changes, maintaining the oil level and preventing air from entering the tank.
Temperature gauge:
A temperature gauge is a monitoring device used to measure transformer oil and winding temperatures. It provides important information about the operating conditions of the transformer and helps prevent overheating.
Conclusion:
Transformers consist of various essential parts, each with specific functions that contribute to their efficient operation and safety. From the core and windings that facilitate voltage conversion in the tank and provide mechanical support and electrical insulation, each component plays an important role in ensuring the reliable operation of transformers in a power system. Proper maintenance and monitoring of these parts is essential to extend the lifespan of the transformer and improve its performance in power distribution and transmission networks.
FAQ:
Q1- What is the function of cooling system in transformer?The function of the cooling system in a transformer is to dissipate the heat generated during operation, prevent overheating and maintain a safe operating temperature for efficient and reliable performance.
Q2- How do different types of transformers differ in terms of their key components and functions.Different types of transformers differ in terms of their key components and functions based on their intended applications and voltage transformations. Variations are primarily related to the design of windings, cores, and insulation materials to suit specific voltage levels and requirements. For example, power transformers focus on high-voltage applications, while distribution transformers cater to low-voltage local distribution networks. Similarly, instrument transformers are designed for accurate measurement and protection purposes.
Q3- What are the main components of a transformer?The main components of a transformer are the core, primary and secondary windings, insulation, transformer oil, and a tank for containment and protection.











.jpg)


